
Germany vs. Temu
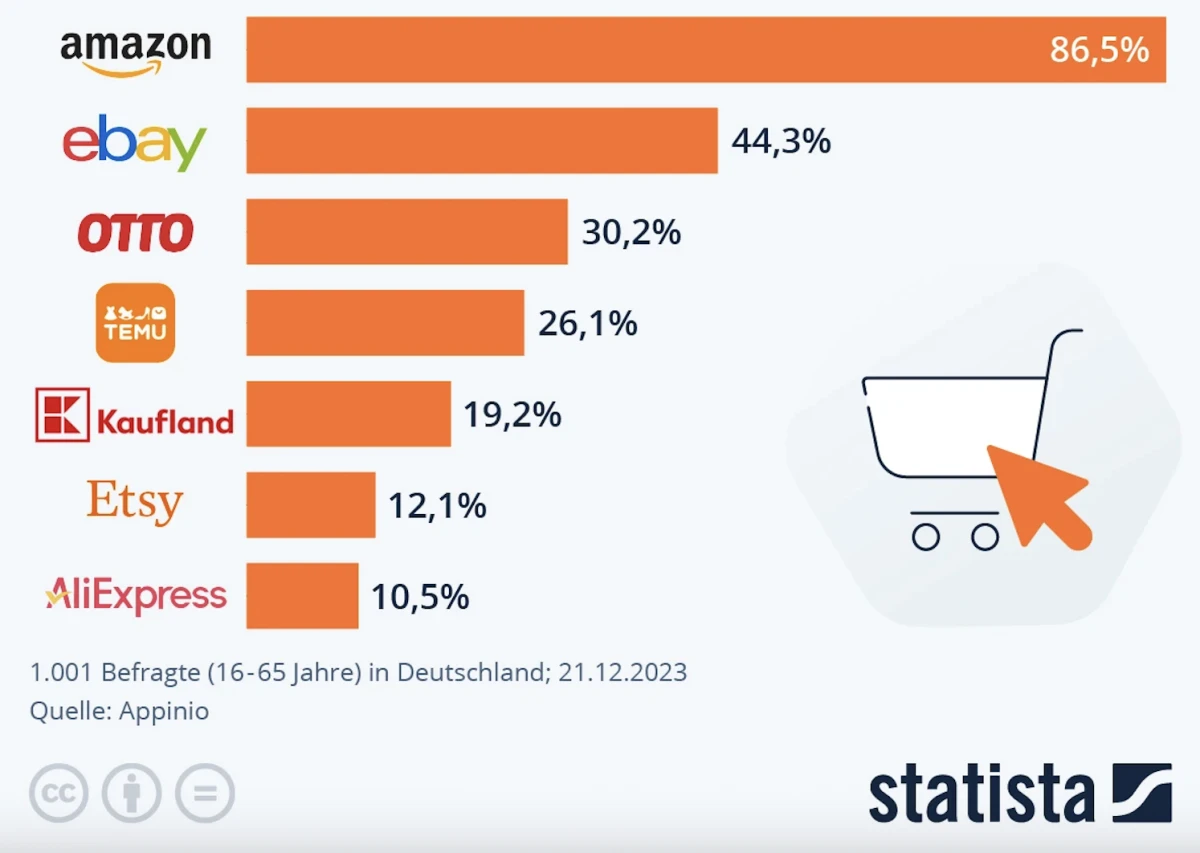
Temu, an online marketplace owned by Chinese company PDD Holdings, has quickly become a major player in the German e-commerce sector since entering the market in 2023. Thanks to aggressive marketing and extremely low prices, it has gained significant popularity in Germany. As early as 2023, one in four Germans reported having shopped on Temu. According to 2023 data, Temu ranked eighth among online marketplaces in Germany, with a gross merchandise value (GMV) of USD 1.04 billion. This rapid expansion has raised concerns among traditional market players such as Amazon, Zalando, and Otto, who are now facing increased competition.
Temu, an online marketplace owned by Chinese company PDD Holdings, has quickly become a major player in the German e-commerce sector since entering the market in 2023. Thanks to aggressive marketing and extremely low prices, it has gained significant popularity in Germany. As early as 2023, one in four Germans reported having shopped on Temu. According to 2023 data, Temu ranked eighth among online marketplaces in Germany, with a gross merchandise value (GMV) of USD 1.04 billion. This rapid expansion has raised concerns among traditional market players such as Amazon, Zalando, and Otto, who are now facing increased competition.
E-Commerce: One in four Germans has already shopped at Temu
Share of respondents who purchased something from the following online marketplaces in the past 6 months
European sellers on Temu
In the summer of 2024, Temu opened up more to sellers from the European Union. These sellers are responsible for listing their products, warehousing, logistics, and handling returns. Temu, on the other hand, manages product pricing (although sellers appear to be able to set at least a base price), customer service, and marketing—both on and off the platform.
Temu currently charges no registration fees, no sales commissions, no advertising costs, and no monthly fees. According to Zixia Yi, these conditions are expected to remain unchanged in the future.
Selling on Temu works as follows: sellers set a minimum price that corresponds to the lowest price on Amazon, while the platform determines the final selling price. If a product is sold at a higher price than the minimum set by the seller, the difference between the two is retained by Temu.
Can a Czech online store sell on Temu?
Yes, but only indirectly for now.
Currently, only companies registered in Germany, France, Italy, Spain, the Netherlands, and the United Kingdom are eligible to sell on Temu.
Entry requirements:
✔ Business registration in one of the eligible countries
✔ Local VAT ID for the target market
✔ Invitation-only program – sellers must contact a Temu representative and be approved
For Czech online retailers without a business entity in these countries, entering Temu is complicated.
An alternative could be setting up a company in Germany or working with an intermediary.
How Temu Is Affecting EU Online Stores in Germany
Rising CPC Costs on Google and Facebook
Temu is heavily investing in paid advertising across Facebook, Google Ads, TikTok, and other channels. The result? Auction-based click prices (CPC) in Germany are soaring. For EU-based online stores, this means more expensive ad campaigns and significantly higher customer acquisition costsPrice War and Margin Pressure
Temu is reshaping customer expectations—German consumers are increasingly looking for ultra-cheap deals. Traditional e-commerce stores are forced to lower their prices to stay competitive, which compresses profit margins and raises the marketing return on investment (ROI) threshold.
Impact on Organic Search Visibility
Temu also invests heavily in SEO, dominating organic search results. This makes it harder for smaller or mid-sized EU online stores to rank on Google, decreasing their visibility and traffic without paid support.
Regulatory Issues and Germany’s Policy Reactions
The growing popularity of platforms like Temu and Shein has raised concerns regarding compliance with European standards in areas such as product safety, consumer protection, and fair competition. The German Ministry for Economic Affairs developed the "E-Commerce Action Plan" aimed at strengthening enforcement of existing regulations related to product safety, environmental protection, consumer rights, as well as customs and tax compliance.
The Action Plan, adopted by the German government on January 29, 2025, outlines several proposals for regulating third-country marketplaces like Temu and Shein. The Ministry is actively working with the European Commission and EU member states to implement these measures at the EU level. The first regulatory steps are expected to be approved within 2025.
The plan is structured into 3 main categories and 13 subcategories:
I. Strengthening Market Surveillance and Customs Enforcement
The Action Plan aims to improve market surveillance and tighten customs controls to prevent the import of illegal or unsafe products. A key aspect is enhancing cooperation between surveillance authorities and customs offices to better coordinate the monitoring of online sales and identify problematic goods.
Automated tools will be used to detect and flag non-compliant products, including mystery shopping to quickly expose violations. Customs checks will be reinforced, especially for shipments under EUR 150, which often bypass customs fees.
These measures are designed to enforce existing rules more effectively, helping level the playing field for European e-commerce businesses and curbing unfair competition from China. For Czech sellers, this means Chinese importers will face stricter oversight.
II. Enforcing Platform Compliance
This section of the Action Plan focuses on enforcing already existing regulations concerning online marketplaces like Amazon, Temu, and Shein. Rather than introducing new rules, the goal is to ensure platforms comply with current EU standards for product safety, consumer rights, and fair competition.
A central role is played by the Digital Services Act (DSA), which obliges large e-commerce platforms to actively monitor listings, prevent the sale of illegal or unsafe goods, and ensure supplier transparency. The new measures in the Action Plan aim to strengthen enforcement, meaning greater platform accountability and faster removal of harmful products.
For Czech e-commerce companies expanding into Germany, this could result in a fairer competitive environment, as Chinese sellers would be required to meet higher standards and undergo tighter controls.
III. Enhancing Environmental and Consumer Responsibility
This part of the Action Plan emphasizes sustainability, product safety, and consumer protection. The aim is to ensure that online products comply with EU standards and that customers are better protected from deceptive practices.
E-shops and platforms will need to verify suppliers more thoroughly and ensure quick removal of dangerous items. A digital product passport is expected to be introduced, containing information about environmental impact and recyclability. Platform operators would be required to verify the completeness and accuracy of this data.
This step would enable consumers to verify whether a product meets certain criteria. It is also intended to reduce fake discounts, manipulative tactics (such as "last item in stock"), and tighten return policy rules. For Czech sellers entering the German market, this will mean higher administrative burdens, but also the opportunity to compete by focusing on quality and sustainability.
In addition, German consumer organizations like Verbraucherzentrale Bundesverband (vzbv) have issued legal warnings against Temu for practices such as misleading discounts, manipulative design, and a lack of transparency about sellers. These are seen as violations of European consumer protection laws.
At the EU level, the European Commission has launched an investigation into Temu amid suspicions it fails to prevent the sale of illegal products and does not meet DSA transparency requirements. If violations are confirmed, the investigation could result in significant sanctions.
These actions reflect the efforts of German and European authorities to ensure that online marketplaces adhere to legal standards, protect consumers, and foster fair economic competition.
A new German government led by CDU/CSU and SPD officially took office in May 2025, with Friedrich Merz serving as Chancellor. The coalition promotes a market-oriented yet pragmatic agenda, signaling a shift away from ideologically driven interventions. While the new government is unlikely to support direct restrictions on Chinese platforms such as Temu like advertising bans or functional limitations it is expected to maintain a strong focus on regulatory compliance. This includes strict enforcement of consumer protection laws, product safety standards, and a revision of tax advantages that currently benefit non-EU marketplaces. The approach reflects a strategic effort to defend fair competition and safeguard EU norms without resorting to sweeping restrictions.
Temu as a Geopolitical Challenge
Temu poses a significant geopolitical challenge for Europe, encompassing several key dimensions:
Economic dominance and unfair competition:
Through extremely low prices and aggressive marketing, Temu is rapidly gaining market share, creating unequal conditions for European businesses. This strategy risks increasing Europe’s dependency on cheap imports from China and undermining local manufacturers.
Security risks and data protection:
The Temu app collects extensive user data—including contacts, location, and microphone access—which is sent to servers in China. This raises serious concerns regarding cybersecurity and the privacy of European users.
Forced labor and ethical concerns:
There are widespread concerns that some products sold on Temu may originate from supply chains involving forced labor, particularly in the Xinjiang region of China. This raises serious ethical and legal questions regarding human rights compliance.
Dependence on Chinese technology and loss of strategic autonomy:
The growing popularity of Chinese platforms like Temu could increase Europe's technological dependence on China, potentially threatening the region’s strategic autonomy in key areas.
These factors underscore the need for careful assessment and regulation of Chinese e-commerce platforms to safeguard European values, security, and economic interests.
Conclusion
Temu’s rapid expansion in the German market brings more than just low prices for consumers. It also raises serious economic, security, and ethical concerns. By pursuing an aggressive business model, Temu disrupts fair competition, undermines local businesses, and increases Europe’s dependence on Chinese imports.
Cybersecurity and data privacy risks are equally pressing, as the platform collects large volumes of sensitive user information. Furthermore, there are growing ethical concerns related to supply chain practices, including the potential use of forced labor.
Without stricter regulatory oversight, Temu could weaken European consumer protection standards and further consolidate China’s economic influence. This highlights the urgent need for European regulators to maintain a balance between keeping markets open and protecting strategic interests.

How we can help you
Our team will help you with the first steps of your expansion as well as long-term marketing strategies.
